Table of Contents
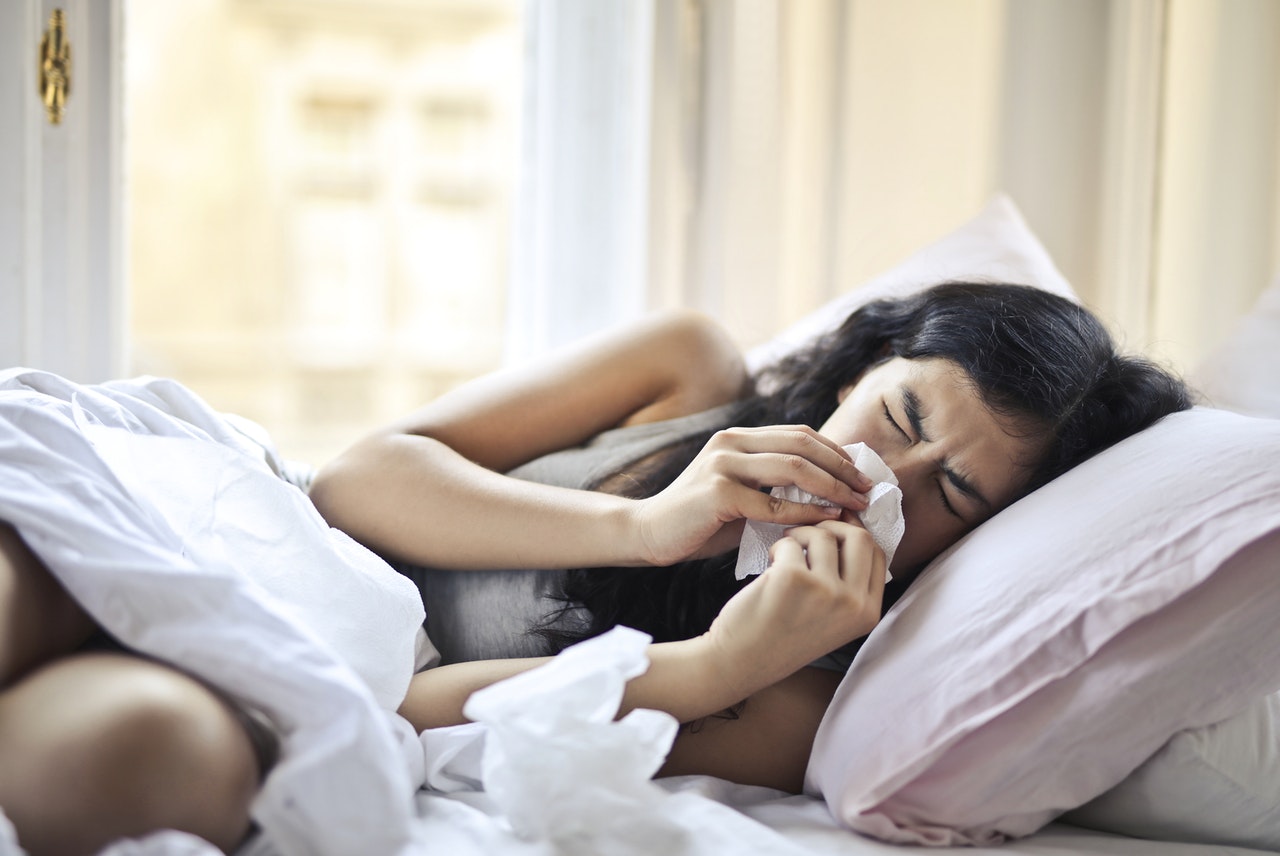
What do you mean by Viral Fever?
Most people’s body temperature is about 98.6 ° F (37 ° C). Any degree above this is considered a fever. Fevers are a sign that your body is fighting some bacterial or viral infection.
Viral illness is any fever by an underlying viral sickness. A type of viral infections can affect humans, from the common cold to the flu. A symptom of fever is many viral infections. However, some viral diseases, such as dengue fever, can cause a higher temperature.
Learn more about viral fevers, including common symptoms and treatment options.
Symptoms Of Viral Fever
Its temperature ranges from 99 ° F to over 103 ° F (39 ° C), depending on the underlying virus.
If you are suffering from viral fever, you could have some of these general symptoms:
- Shaking chills
- Sweating
- Dehydration
- Headache
- Muscle aches and pains
- Feeling of weakness
- Loss of appetite

Causes Of Viral Fever
An infection causes viral fever with a virus. Besides, viruses are tiny infectious agents. These infections are multiplying the cells of your body. Illness is your body’s to fighting a virus.
Many viruses are sensitive to changes in fever. Its increase in your body temperature makes you less favorable to infections.
There are many ways you can get infected with viruses, including:
Inhalation
Suppose someone with viral infection is sneezes or coughs near you. So you can breathe in the droplets that contain the virus.
Examples of viral inhalation infections include the common cold or flu.

Ingestion
Food and drinks can contaminate these viruses. So if you eat them, it can develop an infection.
Examples of viral infections by ingestion include norovirus and enteroviruses.
Stings
Insects and other animals can carry viruses. So if you get stung, you can develop an infection.
Examples of viral infections caused by bites include dengue fever and rabies.

Diagnosed With Viral Fever
Both viral and bacterial infections cause similar symptoms. So to diagnose a viral fever, a doctor usually begins by ruling out a bacterial infection. Therefore you can also do this by considering your symptoms and medical history and taking samples to test.
If you were suffering a sore throat, you could use a swab on your throat to rule out the bacteria that cause strep throat. Thus if the sample is negative, you may have a viral infection.
You can also take a sample of blood or other body fluid to check for specific markers. It could indicate a viral infection, such as the white blood cell count.
Treatments Of Viral Fever
In most cases, viral fevers do not require any specific treatment. Unlike bacterial infections, these do not respond to antibiotics. Instead, treatment usually focuses on relieving your symptoms. Conventional treatment methods include:
- Rest as much as you can.
- Drinking enough fluids to stay hydrated and replenish fluids lost when you sweat.
- Taking antiviral medications.
- Take a warm bath to lower your body temperature.
- Buy Tamiflu now.
Check The Doctor
In many cases, viral fever is not something to worry about it. But if you have an illness that reaches 103 ° F (39 ° C) or higher, to call a doctor. So you should call a doctor if you have a baby with a rectal temperature of 100.4 ° F (38 ° C) or higher. Also, learn more about managing fever in babies.
If you have a fever, monitor the following symptoms, all indicate the need for medical treatment:
- Severe headache.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Chest pain.
- Abdominal pain.
- Frequent vomiting.
- A rash, especially if it gets worse quickly.
- Stiff neck, especially if you have pain when you lean forward.
- Confusion.
- Seizures or Epileptic fits.
Conclusion
Viral fever refers to any temperature that results from a viral infection, such as a cold or dengue fever. Although most viral illnesses resolve on their own within a day or two, some are more serious and require medical treatment. So if your temperature is 103 ° F (39 ° C) or higher, it’s time to call a doctor. If not, try to get as much rest as possible and hydrate yourself.