Table of Contents
What do you mean by Pancrease?
The Pancrease is an organ found in the intestines. It performs a vital part in turning the food we consume into combustible for the body’s cells. The Pancrease has two chief uses: an exocrine role that helps metabolism and an endocrine use controlling blood sugar.
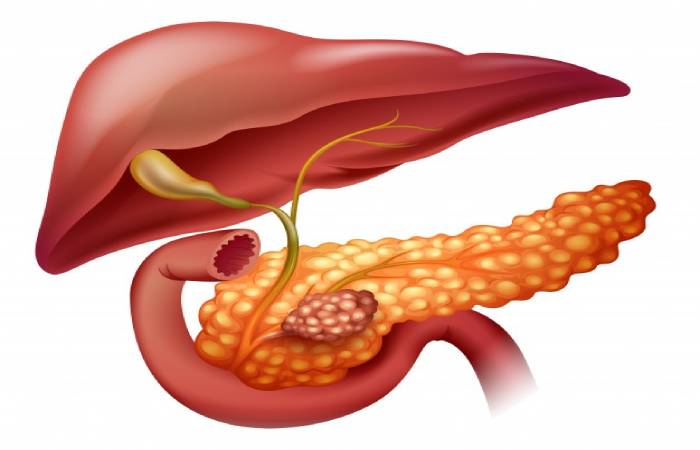
Locating of the Pancrease
The Pancrease resided following the abdomen in the top left abdomen. It encompassed by other means, including the spleen, small intestine, and liver. It is also wet, around six to ten inches extended, and formed like a flattened pear or a fish stretched horizontally over the abdomen.
The whole section, termed the origin of the Pancrease, is located near the abdomen’s core. The head of the Pancrease found that the stomach reaches the initial part of the small intestine at the meeting. This is wherever the belly leaves somewhat ingested food into the intestine, and the Pancrease delivers digestive proteins into these contents.
The center part of the Pancrease termed as the body or neck. The low end is described as the tail and continues to the left side. Many essential blood capillaries surround the Pancrease, the higher mesenteric artery, the above mesenteric vein, the portal vein, and the celiac axis, providing blood to the Pancrease and different abdominal organs.
Nearly all of the Pancrease (95%) comprises exocrine tissue that provides pancreatic catalysts for digestion. The residual tissue consists of endocrine cells described the islets of Langerhans. Those groups of cells seem to like grapes and build hormones that control blood sugar and improve pancreatic secretions.

Details on the Pancrease
Here are some key points about the Pancrease—further particulars in the core article.
- A healthy diet can contribute to maintaining a healthy Pancrease.
- Problems associated with the Pancrease consist of diabetes and cancer.
- The Pancrease is an organ with a vital role in digestion and glucose controller.
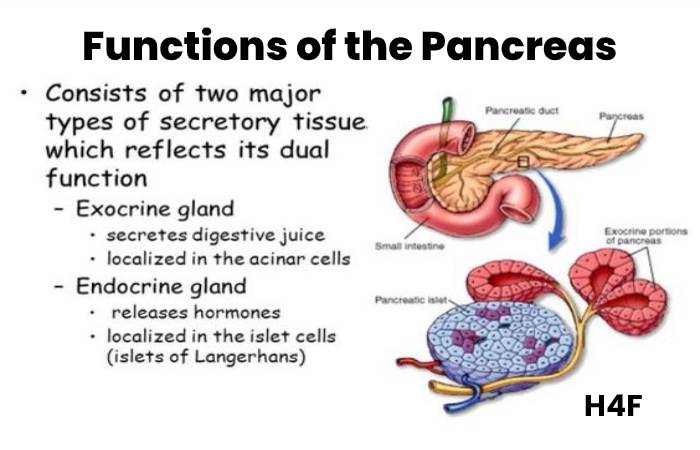
Functions of the Pancreas
A good Pancrease provides the right chemicals in the precise amounts, at the correct times, to absorb the foods we consume.
Exocrine Function
The Pancrease comprises exocrine glands that provide enzymes vital to metabolism. Certain enzymes combine trypsin and chymotrypsin to absorb proteins, amylase for the absorption of carbohydrates, and lipase to crackdown fats. Suppose food joins the abdomen, those pancreatic fluids discharged into a pipe that ends in the ventral pancreatic duct.
The pancreatic tube connects the typical bile channel to make the ampulla of Vater, which found at the front part of the small intestine, named the duodenum. The standard bile channel begins in the liver and the gallbladder and provides added significant digestive fluid called bile. The pancreatic liquids and bile delivered into the duodenum aid the body digest proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Endocrine Function
The Pancrease endocrine segment contains islet cells (islets of Langerhans) that produce and deliver essential hormones straight into the bloodstream. A couple of the principal pancreatic hormones are insulin, which works to more moderate blood sugar, and glucagon, increasing blood sugar. Keeping normal blood sugar levels is essential to vital organs, including kidneys, brains, and liver.
Disorders of Pancrease
Disorders concerning the Pancrease comprise Pancreatitis, precancerous states such as PanIN and IPMN, and pancreatic cancer. Any disease may show various signs and needs other therapies.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis points to an intense or chronic pain of the Pancrease. So it leads to trivial diabetes. Also, pain can happen if a gallstone or cyst forms the center channel from the Pancrease. So Pancreatic fluids will grow in the Pancrease, generating harm to the Pancrease. Also, the Pancrease may begin to absorb itself. Therefore, Pancreatitis can occur because of mumps, gallstones, trauma, alcohol use, drugs, and steroids.
Acute Pancreatitis
is unique, but it requires urgent therapeutic care.
Indications include:
- Fever
- Intense abdominal pain, tenderness, and swelling
- Muscle aches
- Nausea and vomiting
Prompt medication typically is with liquids and painkillers. Thus, sufferers usually do not need to have initially. But if the Pancreatitis is moderate, they begin to have again almost immediately. So if a subsequent disease happened, surgery might be required.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Progress if severe Pancreatitis frequently occurs, occurring in lasting harm. So the most frequent problem is alcohol misuse, and it often concerns middle-aged men.
Signs include:
- Weight loss
- A steadfast ache in the uppermost stomach and back
- Mild jaundice
- Diarrhea
- Diabetes
Hereditary Pancreatitis
This occurs if there is an acquired difficulty in the Pancrease of the intestine. So an individual below 30 years of age may feel repeated severe Pancreatitis, starting to a lifelong ailment. Also, it is a growing state that leads to continuing harm. Therefore, the person might feel diarrhea, malnutrition, or diabetes, pain. So, medication tries to manage grief to reinstate lost enzymes. Also, the genetic examination is accessible for sufferers who might look at danger.
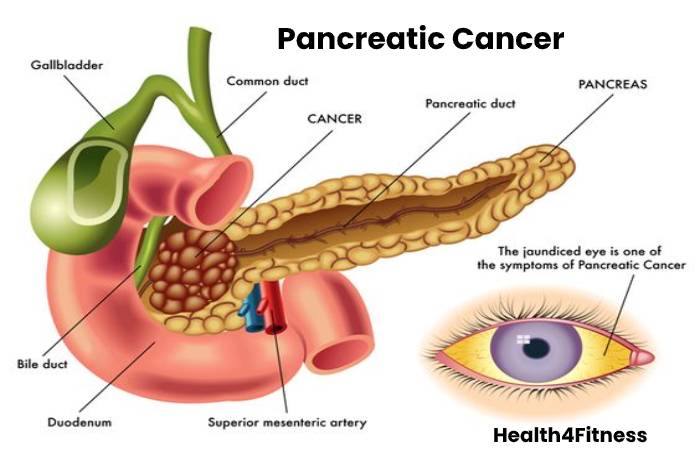
Pancreatic Cancer
Cancer might happen in the Pancrease. So the particular difficulty usually far but is typically connected to smoking or massive drinking.
Additional hazard factors:
- Chronic Pancreatitis
- Diabetes
- Liver problems
- Stomach infections
Indications include:
- Significant weight loss and weakness
- Gray stool or Pale, and surplus fat in the stool
- Agony in the higher belly as the cyst starts against the nerves.
- Loss of nausea, and vomiting, appetite
- Jaundice, skin, eyes yellowing, and darkening of the urine as cancer interfere with the liver’s bile duct and the liver.
Signs may not emerge until the cancer is in the forward phases. So it might late for thriving therapy—the diagnosis for pancreatic cancer points below. But medication involves surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, or a combination of these types. So the palliative approach center on lessening the pain. Besides, Pancreatic cancer is the common cancer problem in men in the United States (U.S.) and the fifth in women. Thus, above 37,000 latest cases, they diagnosed every year.
Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder. So it happens if the immune system strikes and kills the Pancrease’ beta cells to provide insulin not longer. Thus, the precise origin persists desert but might due to hereditary and environmental factors, including infections.
Type 2 diabetes starts when the body’s tissue, fat, and liver cells grow and are inefficient in preparing glucose. So the Pancrease acts by providing additional insulin. However, in time, it could not offer sufficient insulin. Also, the body might not much regulate blood glucose levels.
Additional difficulties that involve:
- Zollinger-Ellison symptoms: A cyst identified as a gastinoma emerges in the duodenum or Pancrease.
- Pancreatic fluid collections: Resultant from a kind of disorder, this leads to pain and fever.
- Pancreatic lumps: These can remove with the help of surgery and if there is a risk of cancer
- Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency: The Pancrease does not create sufficient enzymes.
Pancrease Tests
Physical Examination
By pushing on the belly’s core, a doctor might examine for blocks or intestinal disorders. So he or she can also see for additional symptoms of Pancrease diseases. Also, the pancreatic injury usually spreads to the back.
Computed Tomography Scan
A CT scanner uses various X-rays, and a computer generates accurate pictures of the Pancrease and intestines. Also, the opposite color may be inserted into your arteries to enhance the photos.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic waves produce exact pictures of the stomach. Also, Magnetic vibration cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an MRI that concentrates on the bile system and the liver.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
So, utilizing a camera on a soft tube improved from the mouth to the intestine, a doctor can reach the Pancrease start area. Also, little operational devices utilized to diagnose and manage any Pancrease forms.
Pancrease Biopsy
Both utilizing a needle into the skin or an operational system, a small Pancrease tissue removed to see for cancer or additional circumstances.
Endoscopic Ultrasound
Scrutiny put on the stomach or abdominal ultrasounds, and unadorned sound streams produce pictures by showing off the Pancrease and organs.
Amylase and Lipase
Blood tests revealing advanced levels of these pancreatic catalysts can advise Pancreatitis.
Sweat Chloride Test
A painless electric current excites the skin to sweat, and the chloride in sweat measured. So the people by cystic fibrosis usually produce massive sweating chloride levels.
Genetic Testing
Several various changes of a particular gene may create cystic fibrosis. So the hereditary examination helps to know if a grown-up is an unchanged carrier or if a kid may acquire cystic fibrosis.
Pancrease Treatments
Insulin
Infusing insulin below the skin makes the body muscles for receiving glucose, lowering blood sugar. Besides, insulin created in a lab or filtered of animal sources.
Pseudocyst Drainage
A pseudocyst removed by injecting a tube or needle into the skin into the pseudocyst. Thus, alternately, a tiny tube or stent is set within each the pseudocyst and the abdomen or the small intestine, reducing the cyst.
Pseudocyst Surgery
Sometimes, the operation is needed to remove a pseudocyst. So either laparoscopy or laparotomy might required.
Pancreatic cancer resection (Whipple procedure)
The regular operation to eliminate pancreatic cancer. So in a Whipple method, a surgeon excludes the Pancrease start, the gallbladder, and the small intestine. Therefore, hardly a little part of the belly excluded.
Pancreatic Enzymes
The people by cystic fibrosis or persistent Pancreatitis usually need to get oral pancreatic proteins to substitute those malfunctioning it doesn’t do.
Pancrease Transplantation
An organ donor’s Pancrease transposed into someone by diabetes or cystic fibrosis. Besides, in any patient, Pancrease transplantation remedies diabetes.
Islet Cell Transplantation of Pancrease
Insulin-producing blocks stored from an organ donor’s Pancrease and transposed into type 1 diabetes. So the still-experimental method possibly cures type 1 diabetes.
Pancreatic Stenting/Pancreatic Endotherapy
A stent put in a small or blocked pancreatic tube to stretch it or remove excess fluid. Besides, it utilized to lessen strain.
Maintaining a Healthy Pancrease
Developing a well-balanced diet and withdrawing smoking and extreme drinking helps to keep it healthy.
The National Pancreatic Foundation Suggests
- Drinking plenty of water to keep hydrated
- Drinking no higher than 20 grams of fat a day
- Avoiding alcohol
A fasting intake can trigger the Pancrease to reform itself, which could assist people with diabetes, according to animal research written in February 2017. Also, fast involves eating far some calories than routine for some days.
The National Pancreatic Foundation recommends a similar plan for people who are feeling a flareup of pancreatic injury. So they recommend using a pure fluid diet for 1 to 2 days, including cranberry and grape juice, broth, gelatin, apple.
A fast may not give all the essential nutrients for wellbeing. So following fasting, one should guarantee they eat a nutritious diet to get for nutrients dropped. Also, fasting should addressed with a doctor.
