Table of Contents
Overview of Glucose Challenge Test
The glucose challenge test estimates your body’s answer to sugar (glucose). Also, the glucose challenge test done during pregnancy screening to gestational diabetes — diabetes that occurs when fertility.
The glucose challenge test performed in a couple of steps. Primary, you take a sugary liquid. Then, after one hour, so that your blood sugar level estimated. The outcome of the glucose challenge test shows whether you may possess gestational diabetes. If the examination outcomes are over ordinary, you require an additional examination to ascertain the analysis.
What is the Glucose Challenge Test or GCT Test?
Glucose Challenge Test or GCT is the method of estimating your body’s effect on sugar or glucose. Also, it is a non-fasting examination, which implies you must not fast prior to the study. You relax for an hour, and later a blood analysis done to assess the blood sugar levels. The consequences can give normal, low, or high sugar levels.
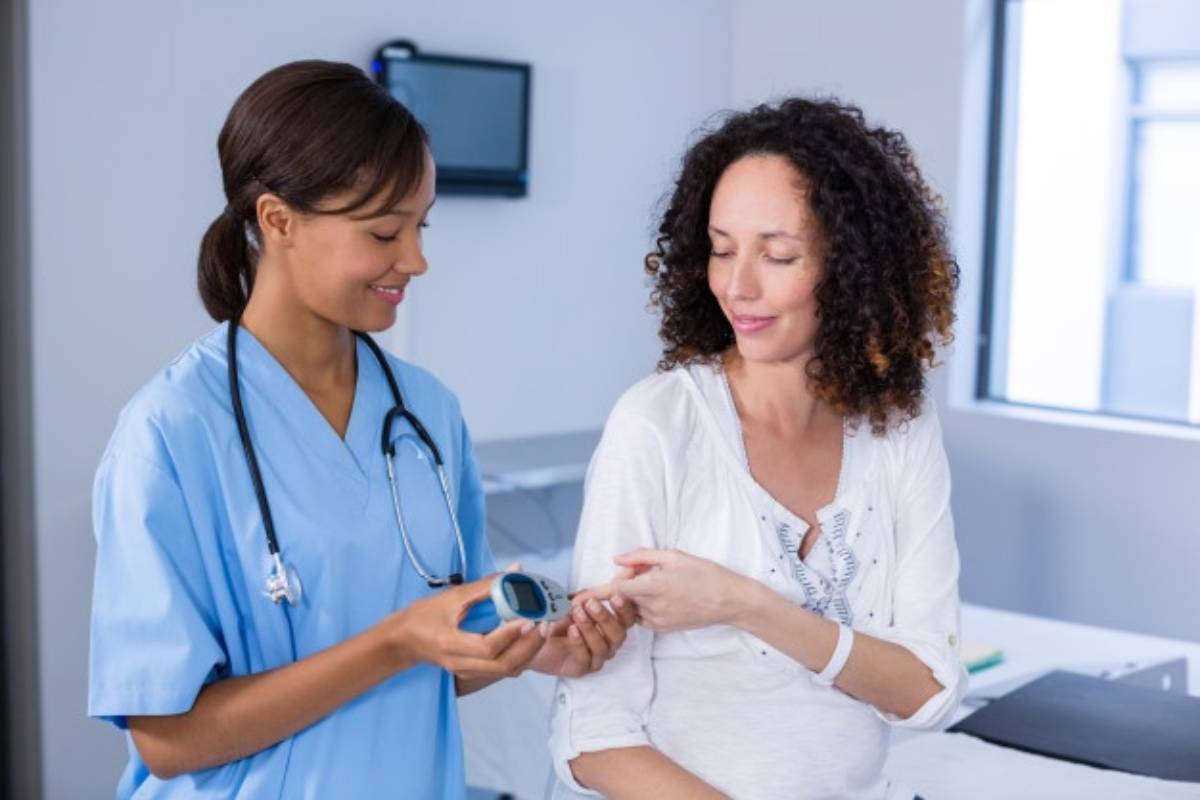
Who Needs To Take Glucose Challenge Test
Suppose a usual urine test reveals high glucose levels, a glucose challenge test done shortly after. In some instances, it did earlier the 24th week. Gentlewomen, often the by significant BMI (Body Mass Index) or a family records of diabetes, require to get the glucose challenge test. More adult pregnant ladies, after 35, also should get the test.
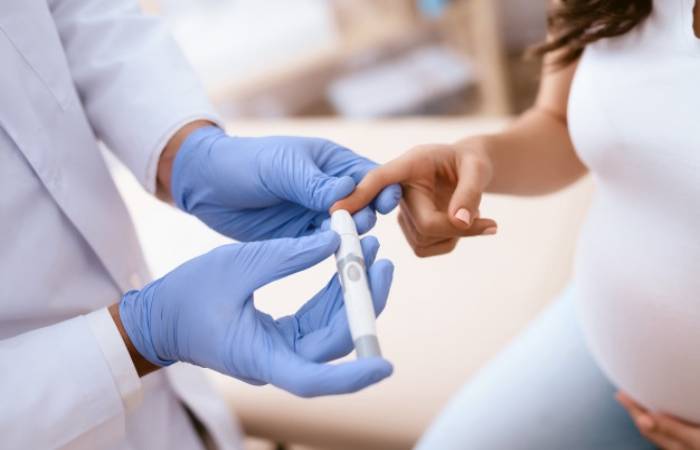
Why GCT Done?
The glucose challenge test used to monitor gestational diabetes. The test generally done between weeks 24 and 28 of pregnancy.
However, it did as soon as your primary fetal appointment if you’re at a significant uncertainty of gestational diabetes over obesity, private past of gestational diabetes, a blood records of diabetes, or additional circumstances. Unusual examination ends beginning in pregnancy force mean that you possess pre-existing type 2 diabetes that wasn’t before notice, relatively than gestational diabetes.
Most utmost women that hold gestational diabetes produce normal babies. But, out precise control, gestational diabetes might begin to many pregnancy complexities, so as preeclampsia or excess fetal growth, which may raise the chance of birth traumas or indicate a C-section birth.
Is fasting Needed for the GCT test?
While the test, the mom suggested drinking a sugary juice (glucose) and later will own blood extracted one hour of holding the liquid, as blood glucose levels naturally rise in one hour. Besides, no fasting needed earlier to the test.
Can you Eat Before the GCT?
Do not consume or take anything but water later about 10 o’clock the nighttime earlier. You don’t require to make any particular arrangements earlier the pregnancy glucose challenge examination. So you may have it in the morning. But necessary to sidestep or avoid foods by plenty of sugar, so as donuts or orange liquid.

What Can You Expect
The glucose challenge test carried in two rounds. When you visit your health care provider’s department or lab, you will get to drink five measures (approximately 148 milliliters) of a syrupy glucose liquid comprising 1.8 measures (50 grams) of sugar.
You require to wait in your healthcare provider’s office during setting for your blood sugar level to examine. So think about doing a mild exercise with you. After one hour, a blood specimen secured of a vein in your arm. The blood unit used to estimate your blood sugar level. While once done the glucose challenge test, you may repeat your everyday actions.
GCT Test Normal Range in Pregnancy
Normal Results
Two-Step Testing
The glucose screening test’s typical result is blood sugar equivalent over or less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) 1 hour following drinking the glucose solution. A specific effect suggests you don’t possess gestational diabetes.
Notes: mg/dL indicates milligrams by deciliter, and mmol/L indicates millimoles per liter. Those are two methods to show how enough glucose is within the blood.
If your plasma glucose is more significant than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L), the following measure is the oral glucose tolerance test. This inspection will confirm if you hold gestational diabetes. Most utmost women (about 2 out of 3) who use this examination do not have gestational diabetes.
ONE-STEP Testing
If your glucose level is below the unusual effects detailed here, you don’t hold gestational diabetes.
What Abnormal Results Suggest
Two-Step Testing
Unusual plasma values for a 3-hour 100-gram oral glucose tolerance examination stand:
- 1 hour: more than 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L)
- 2 hours: larger than 155 mg/dL (8.6 mmol/L)
- 3 hours: higher than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L)
- Fasting: more than 95 mg/dL (5.3 mmol/L)
One-Step Testing
Irregular body fluid values for a 2-hour 75-gram oral glucose tolerance examination remain:
- 1 hour: greater than 180 mg/dL or (10.0 mmol/L)
- 2 hours: larger than 153 mg/dL or (8.5 mmol/L)
- Fasting: more than 92 mg/dL (5.1 mmol/L)
If just a unit of your blood glucose effects in the oral glucose tolerance test is more significant than usual, your provider may advise changing any of the foods you ingest. Then, your provider might examine you over after you have adjusted your food. If more extra than one of your blood glucose results are more significant than usual, you must have gestational diabetes.
GCT or Glucose Challenge Test in Pregnancy
The glucose challenge test or GCT lasted for an hour and carried routinely performed in pregnancy to screen for gestational diabetes mellitus. Also, very significantly, it recently developed and that the GCT can also foretell a woman’s last chance of cardiovascular disease, though an explanation of this connection is not clear. In this connection, we assume that a vast GCT may recognize women with opposite unidentified cardiovascular type. Therefore, we try to assess the relationship between antepartum GCT and postpartum cardiovascular hazard agents.
OGCT Test
An Oral Glucose Challenge Test (OGCT) is a brief version of the OGTT used to examine pregnant women’s gestational diabetes symptoms. It can be performed at any point of the day, not on a bare belly. The examination comprises 50 g of glucose, with the recording after one hour. To determine whether a 50 g oral glucose challenge test (OGCT) is a helpful screening examination for pregnant women 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.

Method
A 50 g OGCT test conducted to 307 unselected women at 24–28 weeks of pregnancy. During venous plasma glucose (VPG) collection following 1 h was >7.8 mmol/l, OGCT was actual. Women with an accurate OGCT felt a 2 h 75 grams oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) as an affirmative analysis of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. During starving and 2 h post, 75 g OGTT values held >5.5 mmol/I and >8 mmol/l. Women did consider diabetes.
Glucose Challenge Test or GCT Normal Range
Consequences of the glucose challenge test provided in millimoles per liter (mmol/L) or milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
- If the blood sugar level under 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) recognized normal.
- A blood sugar level of 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) or more above might mean gestational diabetes.
Any hospitals or labs do a more moderate start of 130 mg/dL (7.2 mmol/L) while screening or testing for gestational diabetes. Assume the consequences of your glucose challenge test show the chance of gestational diabetes. So in that situation, your health care provider will do an additional test — usually the glucose tolerance test — to discover the examination.



