External otitis, diffuse external otitis, or swimmer’s ear is inflammation that affects the skin of the external ear canal, usually from a bacterial or fungal infection.
It is widespread in summer and mainly affects children, the elderly, and the population with cognitive deficits. But It is not severe, And it is painful and causes a temporary disability.
Table of Contents
Causes Of External Otitis
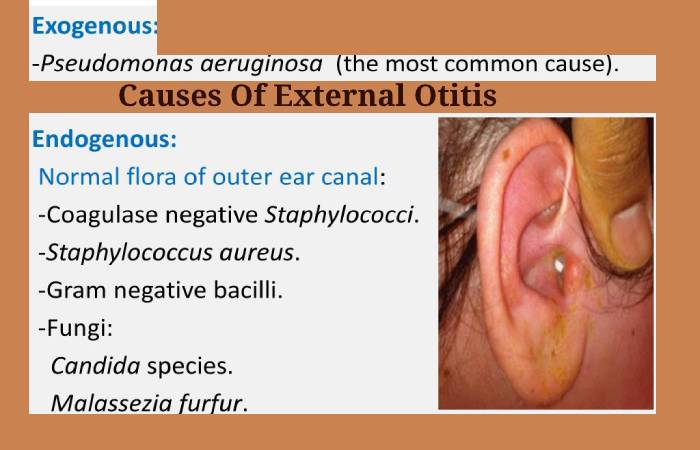
The infection caused by otitis externa or swimmer’s otitis is usually caused by moisture accumulation trapped in the external auditory canal.
So that connects the external ear, where hearing begins, to the inner ear or middle ear.
Under normal conditions, ear wax from the external ear canal forms an oily protective barrier with antibacterial and antifungal activity.
But when there is an alteration, this barrier, for example, by accumulating humidity from showers, baths, thermal baths, swimming pools, environments, or humid climates.
Besides the proliferation of microorganisms. Such as ‘Staphylococcus aureus,’ ‘Pseudomonas aeruginosa’ and even ‘Candida.’ cleaning the ears for earwax removal can also disrupt that protective layer.
There Are Several Types Of External Otitis:
According to a Top ENT Doctor in Dubai, external otitis is not something you should take lightly. If you are suffering from any discomfort in your ears, you should immediately get in touch with an ENT at the earliest. This is because external otitis is left alone, can lead to dangerous and serious consequences.
Diffuse External Otitis: It is the most frequent and usually occurs in children between five and twelve years old. It is also frequent in swimmers.
Localized External Otitis: It is produced by forming a boil in the external auditory canal and usually appeared by ‘Staphylococcus aureus.’ There is pain, hearing loss, redness, and swelling in the wall of the ear canal.
Otomycosis or External Fungal Otitis: It produced by saprophytic fungi such as ‘Candida albicans’ or ‘Aspergillus niger.’ They can appear from prolonged treatment with antibiotic ear drops or continued exposure to water. This changes the pH of the outer ear canal and, together with the heat, provides the right conditions for fungal growth.
Eczematous External Otitis: It is dermatitis with redness of the skin, peeling, and itching of the external auditory canal. It is related to atopic, seborrheic, contact dermatitis, lupus, psoriasis, and stress, among other conditions.
Malignant External Otitis: It is aggressive and severe. It produces an infection of the temporal bone, one of the bones of the skull. And which can spread to other tissues in the area and even affect the cranial nerves. Ear pain is very intense and is associated with headaches.
Symptoms Of External Otitis
It usually occurs quickly, usually within 48 hours of severe ear pain (otalgia). Also, serous or purulent discharge from the ear (otorrhea), heat in the area, pain when chewing, and even itching. There is also hearing loss or poor hearing and a feeling of a blocked ear.
Its Diagnosis
In addition to completing a questionnaire to obtain the description of symptoms by the pediatrician, family doctor, emergency physicians, and otolaryngologists.
Also, they perform an ear examination with an otoscope. A sample of secretions or earwax can also be taken with a sterile swab to study under a microscope.
If the eardrum cannot visualize, pediatricians, family doctors, and emergency physicians will refer the case to the otolaryngologist.
If malignant otitis external is suspected, imaging tests such as a scan and computed tomography (CT) will be requested. A culture should do to determine which bacteria cause it and antibiotic sensitivity.
Treatment And Medication Of External Otitis
The Treatments Of Choice For The Different Types:
Diffuse External Otitis: It treated with anti-inflammatories, local heat, and ear drops administered in doses of three drops two or three times a day. It is essential to apply them correctly.
In some cases, oral antibiotics will be necessary. The treatment lasts between seven and ten days. The patient should avoid wetting the affected ear during that time.
Localized External Otitis: It treated with local heat, oral antibiotherapy, and surgical drainage if necessary.
Otomycosis Or External Fungal Otitis: The otolaryngologist performs treatment under a microscope with the aspiration of the fungal filament structures (hyphae) and earwax cotton plugs.
Topical antifungals prescribed for a couple of weeks and will follow up afterward. To prevent recurrences, solutions with boric acid or salicylates may recommend.
Eczematous External Otitis: Baseline dermatological disease treated with topical corticosteroids.
Antihistamines, acidifying drops may prescribed to restore the external ear canal’s pH and desiccants in case of wet fissures.
Given the risk of permanent loss of part of the auditory function (hearing loss), a surgical solution considered: canaloplasty.
Malignant External Otitis.: The initial treatment is the application of a broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotic. Treatment maintained until a second scintigraphy test shows that the infection overcome.
If there are injuries, abscesses, or bone sequestration, debridement surgery may indicate to remove dead, damaged, or infected tissue.
Prevention Of It:
The Prevention Measures Are Crucial :
You have to dry your ears thoroughly after showering, bathing, bathing in the pool or on the beach with the tip of the towel tilting the head to each side to favor the exit of water.
- It is essential to protect the ears with protective caps to bathe on the beach or the pool.
- Chew gum at takeoffs and landings on an airplane trip, and long car trips to avoid the pressure effect.
- Avoid loud noises and at a short distance, especially for a long time.
- Don’t use cotton buds to clean the ears.
